Political System In Poland
Political system in poland. The transition from a mono-party Communist regime to liberal. Poland is a country with a well founded system of democratic government. By Jan Kubik College of Wooster.
Political system also follows a principle of checks and balances which enables all three branches to mutually control each other. Legislative power is vested in the Sejm and the Senate executive power is vested in the President of the Republic of Poland and the Council of Ministers and judicial power is vested in courts and tribunals. Locating the role of the Churches in the conservative political shift in Eastern Europe is essential not least in the case of Catholic Poland.
Poland was a multi-religious and multi-ethnic country national minorities made up about 30 of the general populace. Polands judicial changes and rulings may have set in motion a process that effectively decouples the country from the EUs legal system. The system of parliamentary democracy was first set up by the Small Constitution of 1919 and consequently the Constitution of 1921.
The ruling partys effort to put the domestic judicial system under tighter political control is setting off a European conflagration. Like most of the other governments in the region Poland is governed by a multi-party parliamentary democracy. Tadeusz Mazowiecki became prime minister in September 1989 leading the countrys first democratic government since the end of World War II.
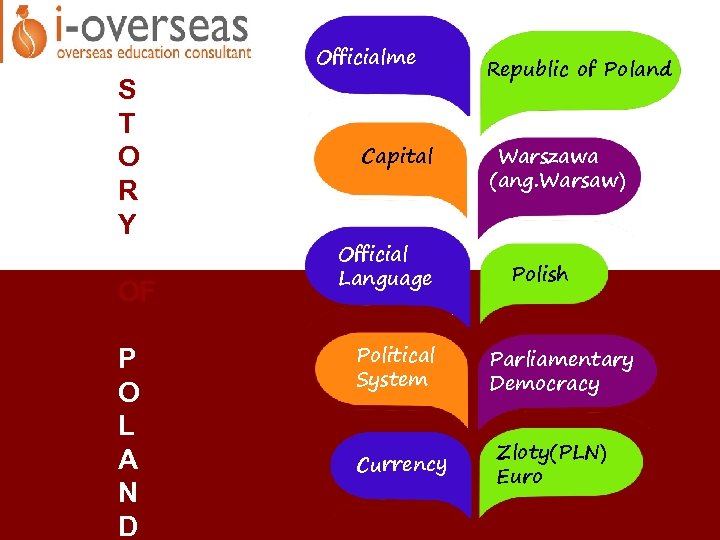
The system of government of the Republic of Poland is based on the principle that there is separation and balance between legislative executive and judicial powers. Polands Kaczyński to resign as deputy prime minister in 2022 Poland Poland seeks to clarify court ruling in EU legal supremacy row. Political Structure of Poland.
Our republic is a multiparty democracy with a two chamber parliament. A Theoretical Reconsideration. The political parties in Poland represent a broad range of public consensus with groups which may be classified as social-democratic liberal conservative national rural-interest or populist.
The postwar government was run as a dual system in which state organs were controlled by parallel organs of the PUWP. The legislative power is held by the lower house of Parliament the Sejm whose 460 members are elected in general proportional elections.
A Theoretical Reconsideration.
Political Structure of Poland. The system of government of the Republic of Poland is based on the principle that there is separation and balance between legislative executive and judicial powers. Poland is a high-income country with a large and diversified domestic economy. With a series of contested judicial reforms and. EU leaders may want to kick their rule-of-law rupture with Poland as far down the road as possible but the disputes legal implications cant be so easily ignored. The rules of functioning of the state are laid down in the Constitution which is the supreme legislative act. The transition from a mono-party Communist regime to liberal. Political Structure of Poland. Poland was a multi-religious and multi-ethnic country national minorities made up about 30 of the general populace.
The transition from a mono-party Communist regime to liberal. Political system also follows a principle of checks and balances which enables all three branches to mutually control each other. The rules of functioning of the state are laid down in the Constitution which is the supreme legislative act. A Theoretical Reconsideration. Polands Russian roulette with the EU. Legislative power is vested in the Sejm and the Senate executive power is vested in the President of the Republic of Poland and the Council of Ministers and judicial power is vested in courts and tribunals. Political administrative and legal system in Poland.






































Post a Comment for "Political System In Poland"